In HTML 5, the <a> tag defines hyperlinks to locations on the same page or other pages on the Web.
The href attribute is the most important attribute of the <a> tag. The href attribute specifies a URL or URL fragment that provides the destination of the hyperlink. “A URL fragment is a name preceded by a hash mark (#), which specifies an internal target location (an ID) within the current document.”2
For example, for creating a link back to the top of the page, you can use the special fragment "top":

If in HTML 5 the href attribute is not specified, the anchor element <a> represents a placeholder hyperlink.
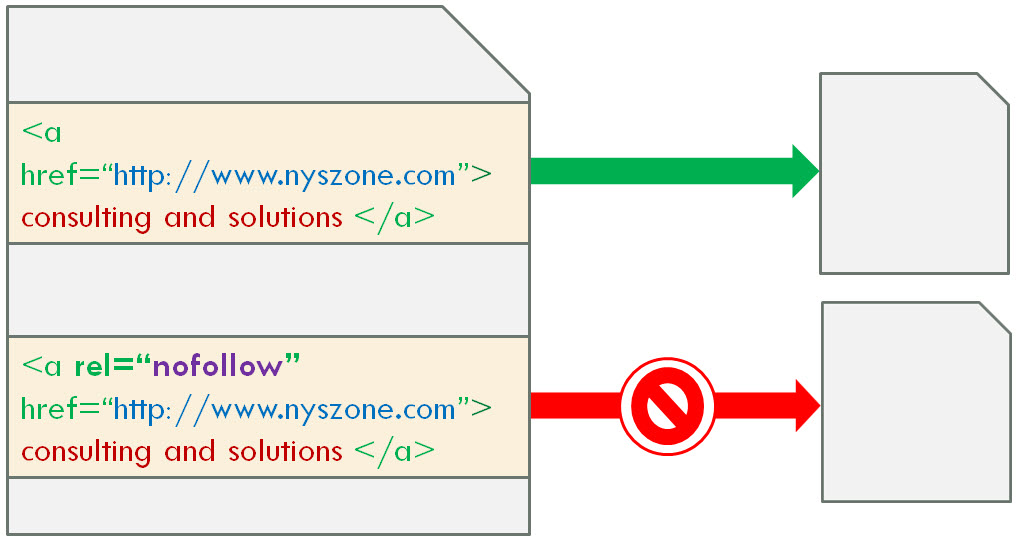
All the time when you link to another website, your linked page gives that website some amount of rank credits. To prevent that, you need to add the rel=“nofollow” attribute to your <a> tag in the HTML code.
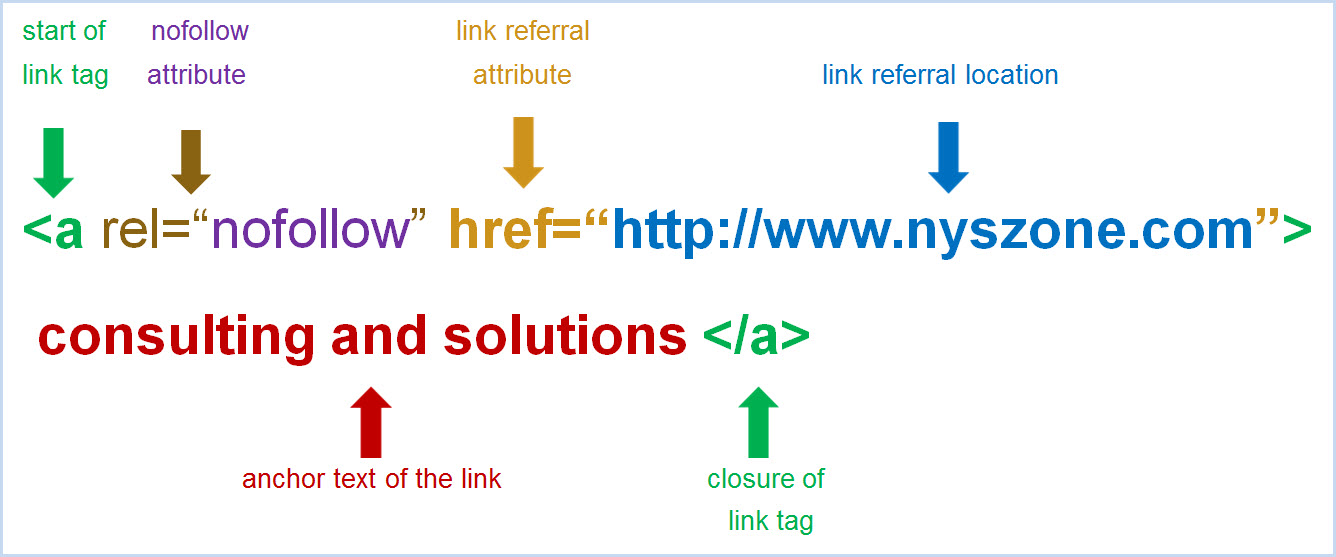
The “nofollow” attribute “specifies the relationship between the current document and the linked document” 3, namely blocks rank credits that your page might give another website. The rel=“nofollow” attribute is only used if the href attribute is present in <a> tag.
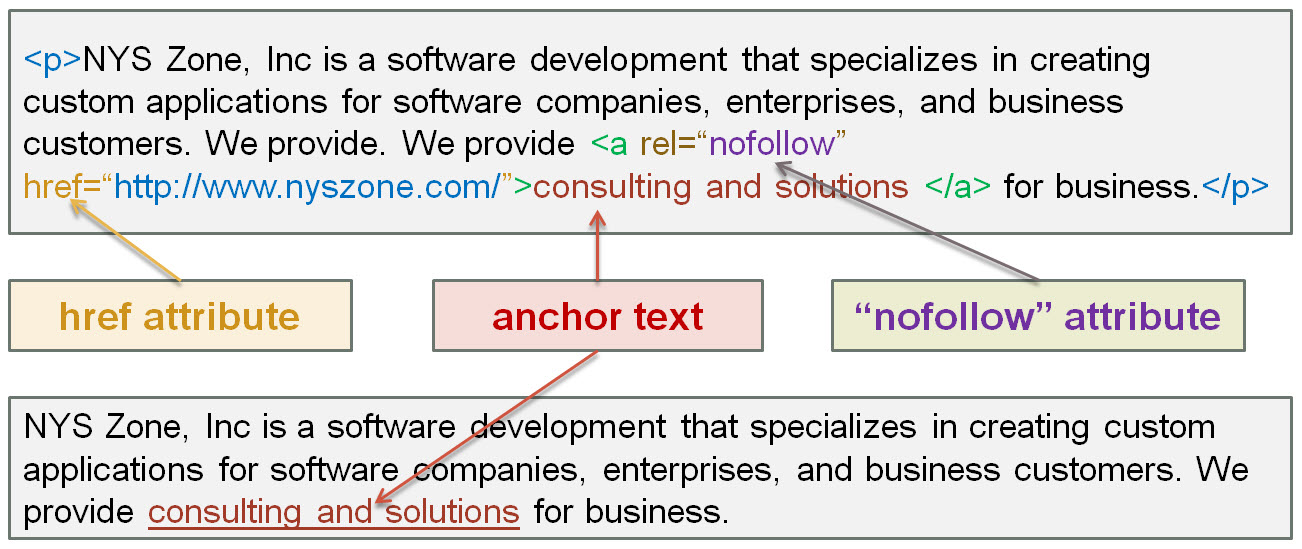
Browsers do not use “nofollow” attribute in any way; however, search engines use it to get more information about a link and to specify that the search spider should not follow that link. “Google does not transfer PageRank or anchor text across these links. Essentially, using "nofollow" causes us to drop the target links from our overall graph of the web.”4
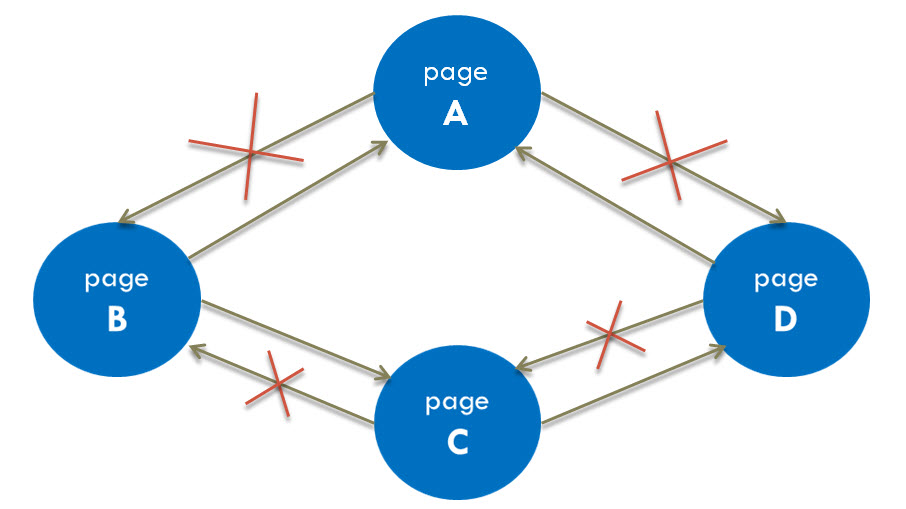
When you are creating your website’s internal links, the “nofollow” attribute helps you to set a crawling way of your pages to Googlebot that allows you to manage rank credits from page to page within your website and prevent a crawling recirculation.
You should make a decision on when to use the "nofollow" attribute for your links and when to allow search engines to follow your links. The primary cases in which you might want to consider using “nofollow” attribute are:
Links are an important attribute of your website, regardless of their “follow” or “nofollow” status. Even if "nofollow" links don't boost the PageRank and don't help with a page’s placement in the search engine results, “nofollow” links still provide referral traffic.
1. “HTML Living Standard” 6 November 2015.8 November 2015. < https://html.spec.whatwg.org/multipage/browsers.html#scroll-to-fragid >
2. “<a>” Mozilla. 16 October 2015, 7 November 2015. < https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/a >
3. “HTML <a> Tag” w3schools.com. 1999-2015. 7 November 2015. < http://www.w3schools.com/tags/tag_a.asp >
4. “Use rel="nofollow" for specific links” Google Search Console Help. 2015. 8 November 2015. < https://support.google.com/webmasters/answer/96569?hl=en >
5. “Hyperlink” Wikipedia: The Free Encyclopedia. 4 November 2015. 8 November 2015. < https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyperlink >